With the Industry 4.0 revolution, enterprise and various industrial applications are equipped with effective wireless networking and IoT solutions. However, challenges persist to meet the specific requirements of these applications in terms of data connectivity, reliability, remoteness, and physical complexity. Today, Wi-Fi is the most dominant unlicensed wireless technology. However, Wi-Fi is not an apt choice to serve specific IoT-related use cases involving remote and mobile deployment. Such use cases demand high coverage, capacity, and efficient transport network/fiber backhaul.
Private 5G networks is envisioned as a promising solution to meet these growing demands.
Private 5G networks provide reliable, low-latency, and secure communication infrastructure that can support the exchange of large amounts of data in real time, which is essential for the development and deployment of new technologies in the manufacturing sector.
Read on, to know what, why, and how Private 5G is fueling Industry 4.0.
What is a Private 5G Network?
Organizations/industries prefer a networking environment that can be controlled, operated, and deployed without the aid of licensed Service Providers (SPs). A private cellular network uses similar technology as the public cellular networks, but it allows an organization/industry to own and control its network to serve a restricted geographical area using dedicated equipment.
Private 5G networks allow industries to own a specific area and operate with licensed, unlicensed, or shared spectrum to enable services within the area. The key bands for private networks are shared access Citizen Broadband Radio Service (CBRS) at 3.5 GHz, global unlicensed 5 GHz band, and MulteFire at 5 GHz.
Organizations can enjoy the benefits of 5G technology such as high-speed data transfer rates, ultra-low latency, and network slicing capabilities to meet specific service requirements.
Why Private 5G is on the Rise and How Private 5G Fuels Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is used mutually with the fourth industrial revolution which signifies an innovative phase in the enterprises and management of the industrial value chain. The evolution to Industry 4.0 is depicted in the image below, which describes the different production methods in each stage.
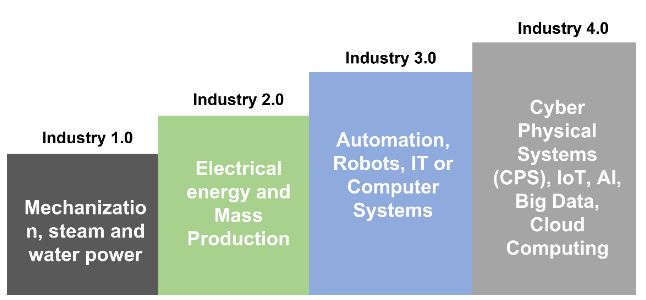
Industry 4.0 realizes digital transformation with key facilitators such as the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), big data analytics, cloud computing, and cybersecurity to create dynamic and competitive environment for enterprises.

Read the blog to learn how Private 5G vs. Wi-Fi 6 are gaining a good deal of hype and discussion around various wireless technologies for realizing digital transformation.
Private 5G networks can be the key enabler of digital transformation, enabling organizations to innovate, automate, and optimize their operations and services. They can help organizations to achieve their business objectives by providing the connectivity, intelligence, and agility required for digital transformation.
Some of the ways in which private 5G networks can support Industry 4.0 are:
High-speed and low-latency connectivity: The 5G capabilities of providing higher data rate up to 10 Gbps, ultra-low latency of less than 1ms and 99.9999 % of higher reliability can enable faster and more efficient production with reduced downtime, and improved product quality and safety.
Reliable and secure communication: Private 5G ensures reliable and secure communication by providing dedicated and isolated network resources that are not shared with other users. This can reduce the risk of cyber-attacks and data breaches and protect critical assets and operations.
Massive IoT support: Private 5G networks support massive IoT deployment, enabling the connection and control of a vast number of sensors, actuators, and devices with diverse requirements, providing real-time monitoring and analysis of production processes, assets, and environments, and enabling predictive maintenance and quality control.
Network slicing and orchestration: Private 5G networks can offer network slicing and orchestration capabilities, allowing the creation and management of multiple virtual networks with different characteristics, such as bandwidth, latency, and security.
Integration with other technologies: Private 5G networks can integrate with other digital technologies, such as AI, ML, edge computing and robotics, to enable advanced automation and intelligence in manufacturing and industrial processes. This can also generate new opportunities for innovation and growth.
Conclusion
Connectivity is what makes Private 5G a key enabler for Industry 4.0. Private 5G networks can deal the connectivity challenges by delivering industries with highly reliable, efficient, controllable, and secure networks designed to a manufacturer’s unique requirements. These capabilities can facilitate industrial sites or enterprises for novel 5G-enabled applications that can digitally transform their businesses in the future.
As Private 5G involves several software defined applications, Calsoft solutions can play a significant role in fully supporting the trend. Calsoft solutions which involves virtualization, networking, and edge computing can aid telecom service providers to create reliable and high-performance Private 5G solutions.
Read further the eBrief to know more about Private 5G Networks
Contact our 5G experts to get answers to your queries related to 5G, Private Networks.
References
[1] “Role of Private 5G Networks in Industry 4.0”, Aeologic
[2] Viswanathan Ramaswamy, “Accelerate your industry 4.0 transformation with Private 5G”, Tata Communications
[3] “Private 5G – Enabling Industry 4.0”, Amantyatech







