The most exciting feature of 5G networks is its ability to provide tailored solutions for wide-ranging use cases such as ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC), enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), and massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC). To support the varying requirements of 5G use cases, network transformation is seen as a key solution. The critical segment of the network transformation is Network Slicing technology!
The network slicing paradigm enables a smart way to partition the physical network into multiple virtual networks for a particular industry, business, or application, to realize multi-tenancy.
In legacy networks, the end-end connection from the user to the application (from user-RAN-Core Network to the Application server) creates a pipe meeting the defined Quality of Service (QoS). The slicing technology guarantees good quality by replacing the legacy single networking with a flexible, on-demand network architecture. The 5G Service Based Architecture (SBA) or 5G cloud-native network becomes an essential enabler for the slicing technology. Know more about 5G SBA through the blog 5G SBA.
Keep reading to explore more about the network slicing concept and its management models!
Selecting the appropriate slice or slice selection is the key characteristic of the network slicing concept. There are various methods for a User Equipment (UE) to select and access an end-to-end slice. 5G helps to dynamically create network instances resulting in multiple logical networks. This logically creates the entire network on demand by enabling multiple connections to multiple users. The end-to-end connection from the end user to the application allocates a dedicated set of physical and virtualized network resources (from end devices, over the RAN, edge, transport, and packet core to the application).
The significant layers of the network slice consist of the service instance layer, network slice instance layer, and resource layer.
- Slice identification and selection is completed through Single Network Slice Assistance Information (S-NSSAI). The NSSAI is a set of up to 8 S-NSSAIs.
- As per 3GPP, an instance of Network Slice – Network Slice Instance (NSI) constitutes a group of network function instances with required compute, storage, and network resources to meet the use case requirements. An NSI constitutes one or many Network Slice Subnet Instances (NSSI).
- NSSI is responsible for managing NSI while providing communication services.
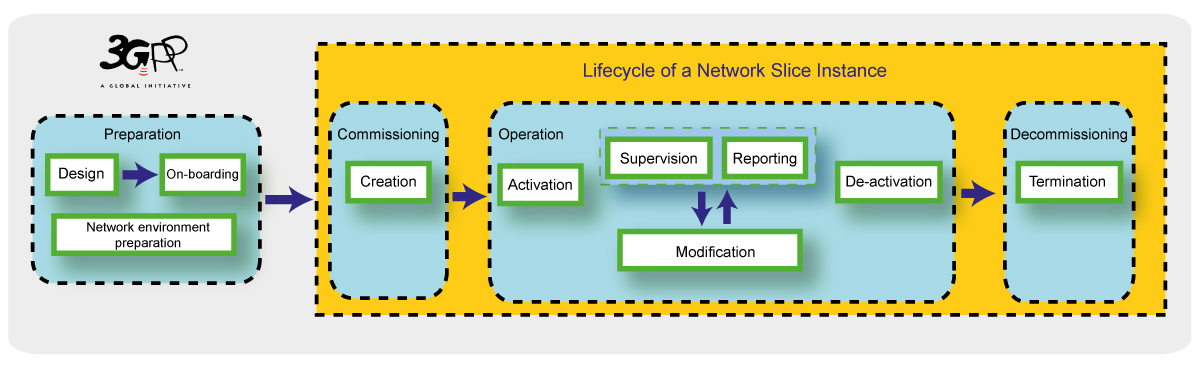
Before understanding the management models of network slicing in 5G, let us see the life cycle of a network slice.
- Preparation: In this stage, the network slice is not created. However, to instantiate a slice, it is required to understand the blueprint of the network like Quality of Service (QoS), reliability, security, and connectivity needed for specific services. This helps to prepare the network environment for the instantiation of a network slice instance.
- Commissioning: This stage includes instantiation and activating the slice. The resources are allocated to meet the slice requirements.
- Operation: Monitoring the performance of slice like checking whether more network function instances are required to meet service requirements or not.
- Decommissioning: Deactivating or ending the slice after use or if not required.
Management Models for Network Slicing
Here, two different management models are explained as shown in the image below:
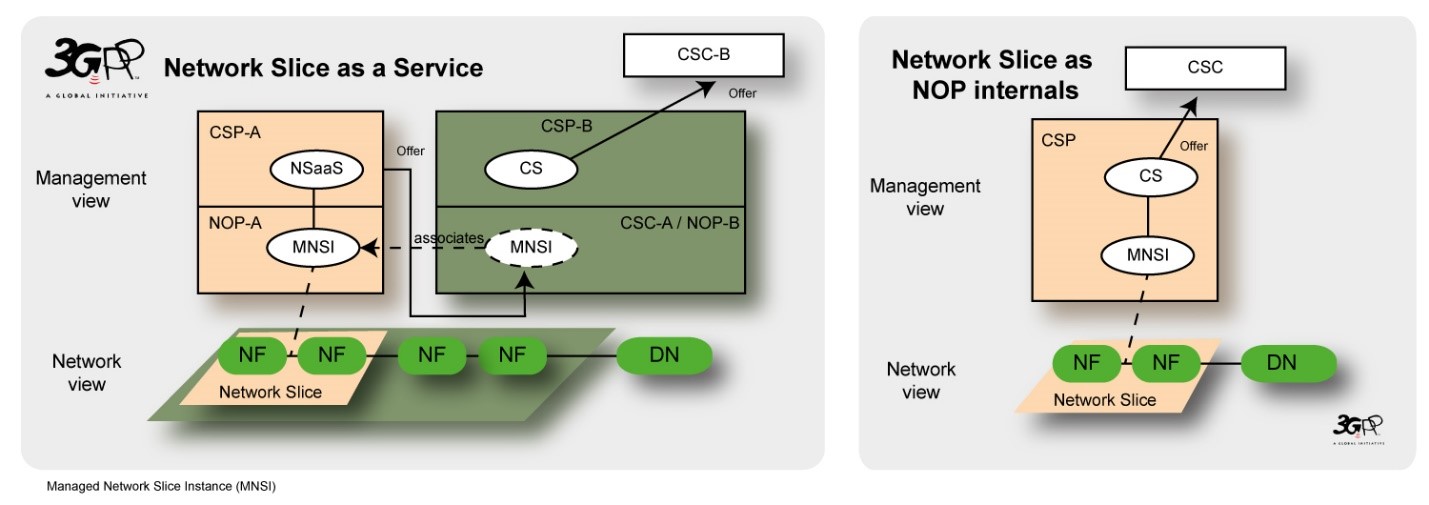
- Network Slice as a Service (NSaaS): Communication Service Provider (CSP) provides NSaaS to its Communication Service Customer (CSC) as a communication service. This service enables CSCs to use, monitor, and manage the network slice instance – MNSI (Managed Network Slice Instance). On top of this network slice instance, CSC can take the role of CSP and deliver Communication Services (CS).
- Network Slices as Network Operator (NOP) internals: CSP deploys slices to deliver services to the customers, hence, network slices are not visible to CSCs. However, CSCs can monitor the service status such as performance (check for any faults), and traffic data using the management exposure interface provided by the service provider.
To know more specific details about slicing and its management models, listen to the podcast 5G: Network Slicing, Its Management, and Orchestration
In a Nutshell
Overall, 5G network slicing is a powerful technology that has the potential to change the way we live, interact, and work. As technology forges ahead and the challenges are addressed, network slicing will become an increasingly principal tool for service providers to meet the needs of their customers.
Calsoft being a “technology first” company, has been actively involved in NFVI automation, Open-Source adoption, Telco Cloud Integration over Open Stack, VNF Engineering, NFV Orchestration & Life Cycle Management, and validation services. Recently, Calsoft got involved in Telco Platform validation with the help of open-source technologies. Talk to our Experts for more details
References
[1] Management, Orchestration, and Charging for 5G Networks (2018). https://www.3gpp.org/news-events/3gpp-news/sa5-5g
[2] 5G Network Slicing. https://stl.tech/blog/the-pros-cons-of-5g-network-slicing/